Bulging Disc: What It Is and How It’s Treated
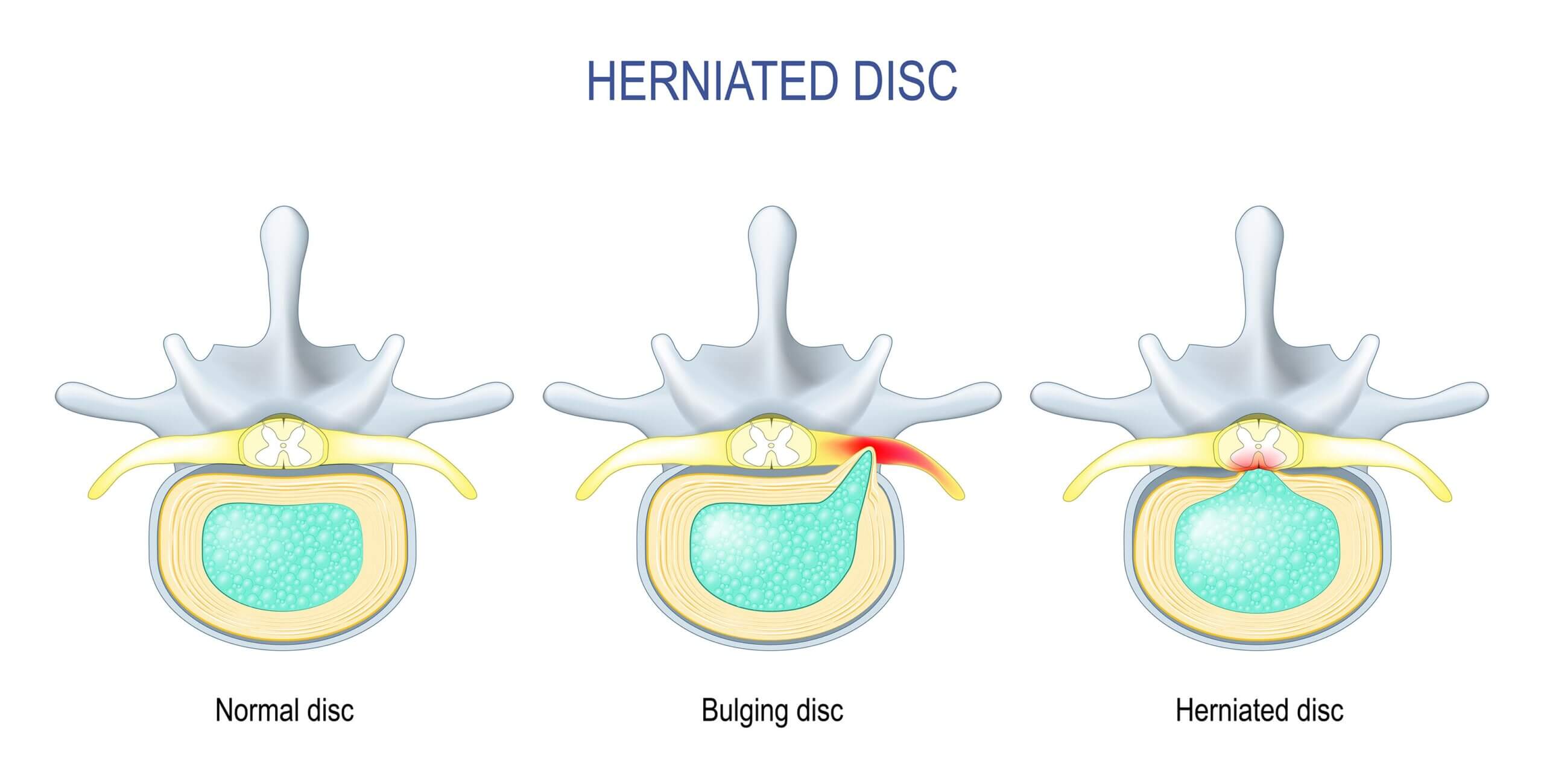
A bulging disc occurs when a spinal disc extends beyond its normal boundary without tearing the outer layer. While less severe than a herniated disc, a bulging disc can still compress nearby nerves and cause pain, numbness, or tingling.
Bulging discs are a common cause of back pain, neck pain, and nerve-related symptoms.
What Is a Bulging Disc?
Spinal discs act as cushions between the vertebrae. Each disc contains:
• Nucleus pulposus – hydrated inner core
• Annulus fibrosus – tough outer ring
When the disc weakens or dehydrates, it may bulge outward evenly.
Common Causes of Bulging Discs
Bulging discs typically develop gradually due to:
• Poor posture
• Prolonged sitting
• Disc dehydration
• Age-related degeneration
• Repetitive stress
• Lack of movement
Bulging Disc Symptoms
Symptoms vary by location.
Lumbar Bulging Disc Symptoms
• Low back pain
• Leg pain or sciatica
• Numbness or tingling
Cervical Bulging Disc Symptoms
• Neck pain
• Shoulder pain
• Arm numbness or weakness
Bulging Disc vs Herniated Disc
A bulging disc pushes outward but remains intact.
A herniated disc involves a tear.
Bulging discs are often more stable and respond well to conservative care.
Can Bulging Discs Heal Without Surgery?
In many cases, yes.
Bulging discs may improve when:
• Pressure is reduced
• Circulation improves
• Inflammation decreases
• Hydration increases
Non-Surgical Treatment Options for Bulging Discs
Non-Surgical Spinal Decompression
Reduces disc pressure and improves fluid exchange.
Disc Rehydration Support
Restores disc hydration and flexibility.
Neurological Decompression
Reduces nerve irritation.
Conservative Rehabilitation
Improves spinal stability and motion.
When Is Surgery Necessary?
Surgery is rarely needed for bulging discs unless there is:
• Severe nerve compression
• Progressive neurological loss
• Failure of conservative care
How the Swolensky Method Addresses Bulging Discs
The Swolensky Method of Disc Rejuvenation integrates:
• True spinal decompression
• Disc rehydration support
• Neurological decompression
• Regenerative stimulation
• Structural stabilization
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a bulging disc become herniated?
Yes, if stress continues.
How long does healing take?
Improvement may occur in weeks; full recovery takes longer.
Is surgery required?
Most bulging discs do not require surgery.
Summary
A bulging disc occurs when a spinal disc extends outward without tearing. Many bulging discs improve with non-surgical care focused on reducing pressure, improving hydration, and calming irritated nerves.
Spinal disc herniation. Difference Between Bulging disc and Herniated Disc. Vector illustration